Extraction and analysis of Citrus Sinensis Seed Oil (CSSO) for prospective use as bio lubricant
Keywords:
ANOVA, FTIR, bio-lubricant, Citrus Sinensis Seed Oil (CSSO) orange seed oil,Abstract
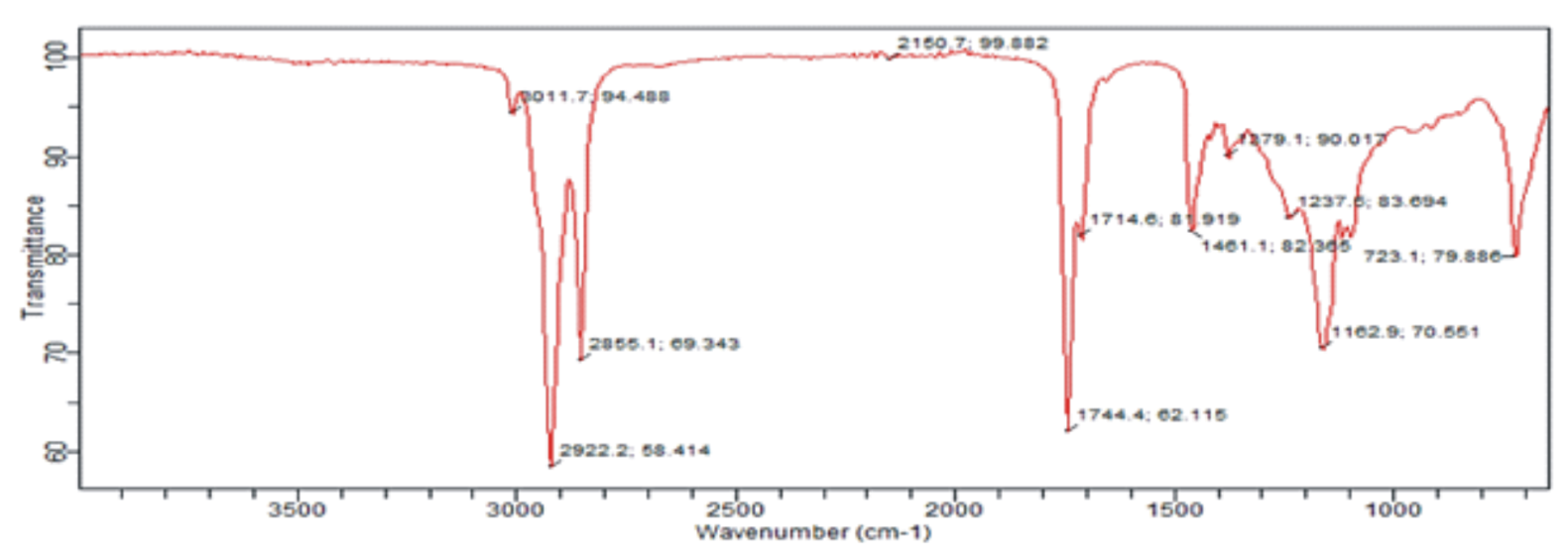
This study investigated oil extraction of citrus sinensis seed oil (CSSO) from Citrus sinensis seed for the production of bio-lubricant. Citrus sinensis seedoil (CSSO) was extracted using Soxhlet extraction method with n-hexane as solvent. The physiochemical properties of the CSSO were examined. Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) was used in the spectroscopy analysis to identify the functional groups. Central Composite Design (CCD) through Response Surface Methodology (RSM) was used to examine the statistical significance of the process parameters. The suitable optimum variables for the extraction process were temperature (65), particle size (0.5), and time (120), with the desirability value of 0.978. The model goodness of fitwas 0.9087 while the model lack of fit and p-value were 40.44 and 0.1005, respectively. The results from the physicochemical properties of the methyl ester from CSS were specific gravity (0.94), kinematic viscosity (46.57mm2 /s) at 40°C, acid value (3.129mgKOH/g), moisture content (0.24%), refractive index (1.4258) at 33°C, saponification value (203.22mgKOH/g), ester value (99.23%), and free fatty acid (1.565mgKOH/g). The spectroscopic analysis showed a number of functional groups which are present in conventional bio-lubricant. The study highlighted the potential suitability of CSSO as bio-lubricant production.