Parametric and Kinetic Study of Hybrid Dye Uptake by Activated Mango Seed Endocarp
Keywords:
Hybrid, Isotherm, Kinetics, Mango-seed, endocarpAbstract
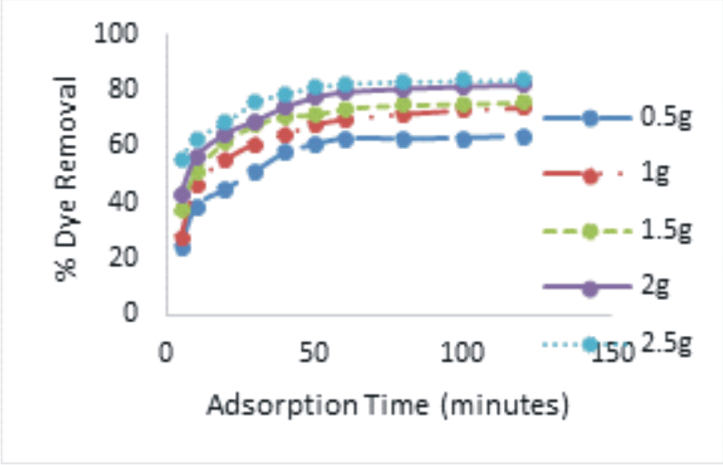
The study investigated the parametric, isotherm, and kinetic modeling for the uptake of hybrid dye (HD) from synthetic textile effluent using mango-seed endocarp activated carbon (MEAC). Scanning electron microscopy (SEM), proximate analysis, Branauer-Emmett-Teller (BET), and Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) analysis was done on the MEAC. The influences of factors: pH, initial concentration of hybrid dye, dosage, and the solution temperature on HD removal were evaluated. The SEM images and FTIR spectra indicated significant porosity and relevant functional groups involved in HD dye adsorption. The results obtained from BET analysis revealed that the specific surface area of MEAC before and after activation and after adsorption were 452.36, 892.16, and 687.894 m2/g, respectively. The results indicate that the adsorption process was better described by the Langmuir isotherm and pseudo-second-order kinetic model. The thermodynamic parameters; enthalpy and Gibbs free energy values were negative showing that the adsorption process was exothermic and spontaneous. The value of entropy obtained was negative. The negative value of entropy relates to a decrease in the degree of movement of the HD molecules adsorbed which suggests a strong affinity between HD and the MEAC. The results reveal the potential of MEAC in HD dye removal and suggest its efficacy for the treatment of textile effluent.