Predictive Analysis of Mild Steel Corrosion Rate during Inhibitive Activities of Chicken Nail Extracts in 2M Sulphuric Acid Solution
Keywords:
Mild steel corrosion, Chicken nail extract, sulphuric acid.Abstract
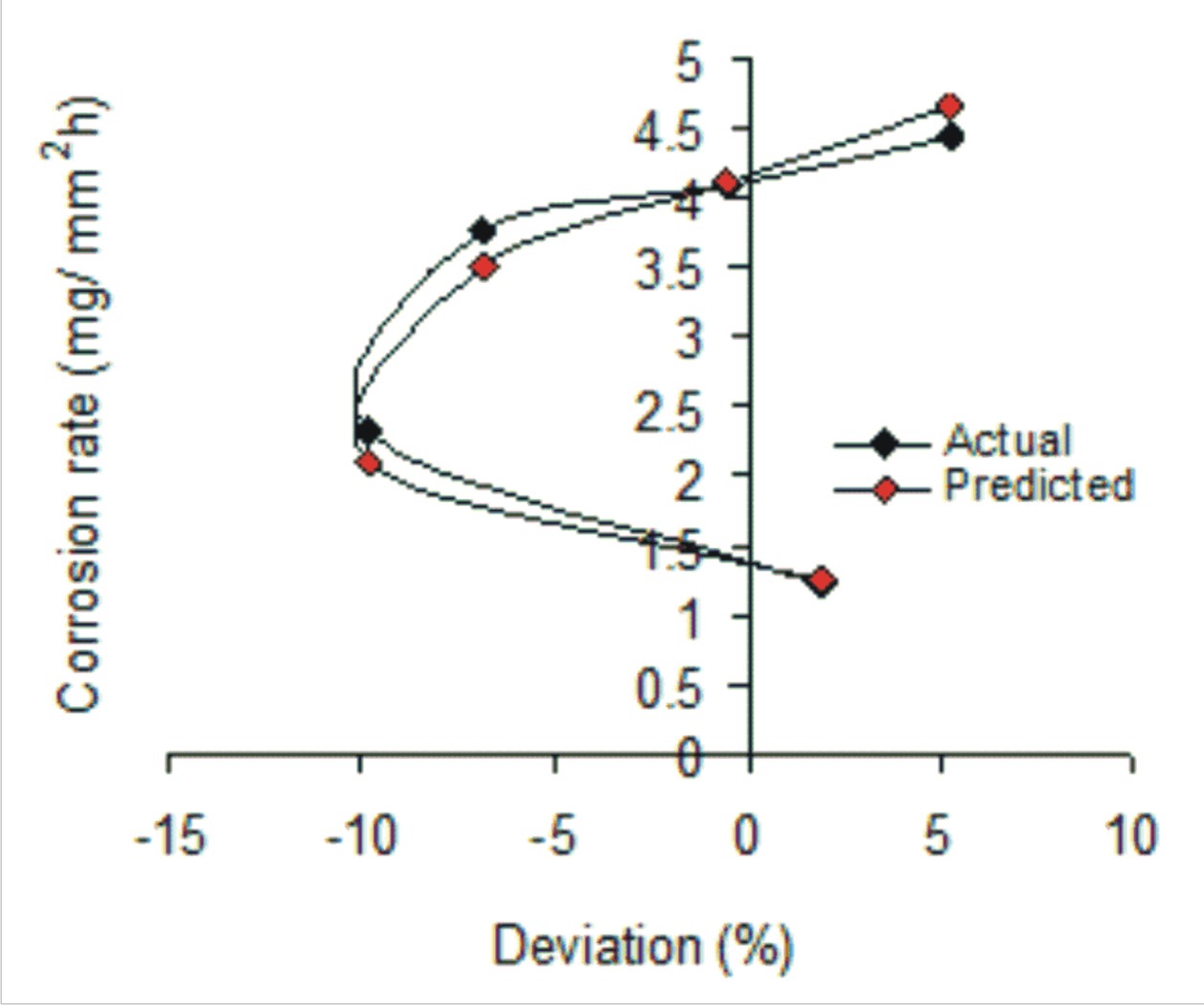
This paper presents the predictive analysis of mild steel corrosion rate during the inhibitive activities of Chicken nail extract in 2M sulphuric acid. The range of process parameters used for reaction temperatures, corrosion rates, inhibitor concentrations and exposure times are 45- 70 (0C), 1.216- 4.422 (mg /mm2 h), 0.67-1.5 (g/l ) and 5.5-8 (hrs) respectively. The mild steel corrosion rate was evaluated to be a direct function of the sum of the natural logarithms of reaction temperatures, inhibitor concentrations and exposure times. An empirical model; Ϧ = 1.3567 ln ϑ + 2.6196 ln β + 3.1095 ln ε – 13.49 predicts the corrosion rate with maximum deviation < 9.85% (from actual results). This translated into over 91.15% operational confidence levels for the derived model. The validity of the model was rooted on the core model expression Ϧ + K = N ln ϑ + S ln β + Se ln ε where both sides of the expression are correspondingly almost equal. The standard error incurred in predicting the model-based corrosion rate relative to values of the actual results is 0.2258. The correlation coefficients between corrosion rate and reaction temperature, inhibitor concentration and exposure time were all > 0.97.