Optimization of Mechanical Properties of Concrete made with Bambara nut shell ash and Quarry dust using Artificial Neural Network
Keywords:
Concrete, Bambara nutshell ash (BNSA), Quarry dust (QD), Artificial neural network (ANN), Optimization.Abstract
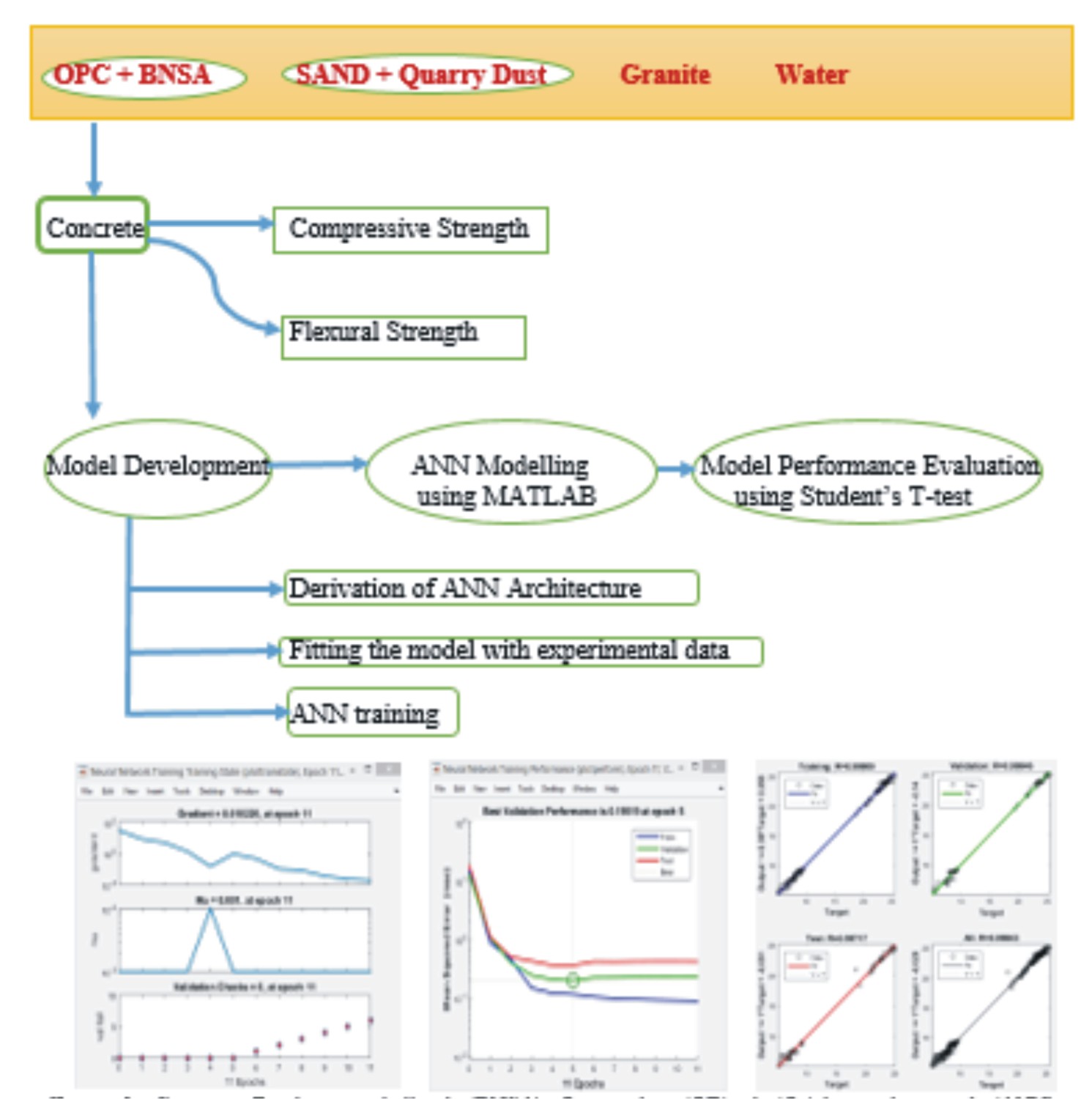
The optimal utilization of valuable resources like money and time through the adoption of artificial neural network (ANN) and its ability to give reliable solutions to problems that are challenging to conventional statistical models, has increased the interest of scholars in using it to estimate concrete properties. In this study, ANN is employed to optimize the compressive and flexural strength of concrete containing Bambara nutshell ash (BNSA) and quarry dust (QD) as partial replacement of cement and sand respectively. This replacement was done at 0 – 50% using 2.5% interval with 1:2:4 mix proportion for 14, 21, 28 and 56 curing days. Two hundred and fifty-two (252) concrete cubes and beam moulds were produced with QD and BNSA. The optimum values were obtained at 22.5% replacement and mix ratio of 0.775: 0.225: 1.55: 0.45: 4. The optimum values of compressive strength recorded from experimental works at 14, 21, 28 and 56 curing age were 24.29 N/mm2, 24.78 N/mm2, 25.14 N/mm2, and 27.36 N/mm2 respectively. Optimum values for the flexural strength were 8.89 N/mm2, 9.32 N/mm2, 9.41 N/mm2 and 13.21 N/mm2. The ANN model had 6 neurons, 10 neurons, and 2 neurons in the input, hidden and output layers respectively. A total of ninety (90) training data set were introduced to the model. 45 samples were used for training, 23 samples each were used for testing and validation. The modelled results were very close to the experimental outcome. 20% replacement was concluded as optimum for structural concrete. The model’s adequacy was further tested using the Student’s T test. The calculated T-value (-2.74 and -3.45) for the compressive and flexural strength of BNSA-QD-concrete were less than that from the T-table (2.09) at 95% confidence level, certifying that the network predictions are suitable and reliable for prediction and optimization of BNSA-QD concrete. The adoption of ANN significantly offers the elbow room for modification during concrete production and attaining required strength. The use of bambara nutshell ash and quarry dust in concrete making are recommended as they improve concrete properties and curtails the issue of poor waste management by transmuting it into wealth