Empirical Analysis of Ceramic Wear Shrinkage Based on the Operational Influence of Firing Temperature and Sustained Porosity
Keywords:
Analysis, ceramic ware shrinkage, porosity, firing temperatureAbstract
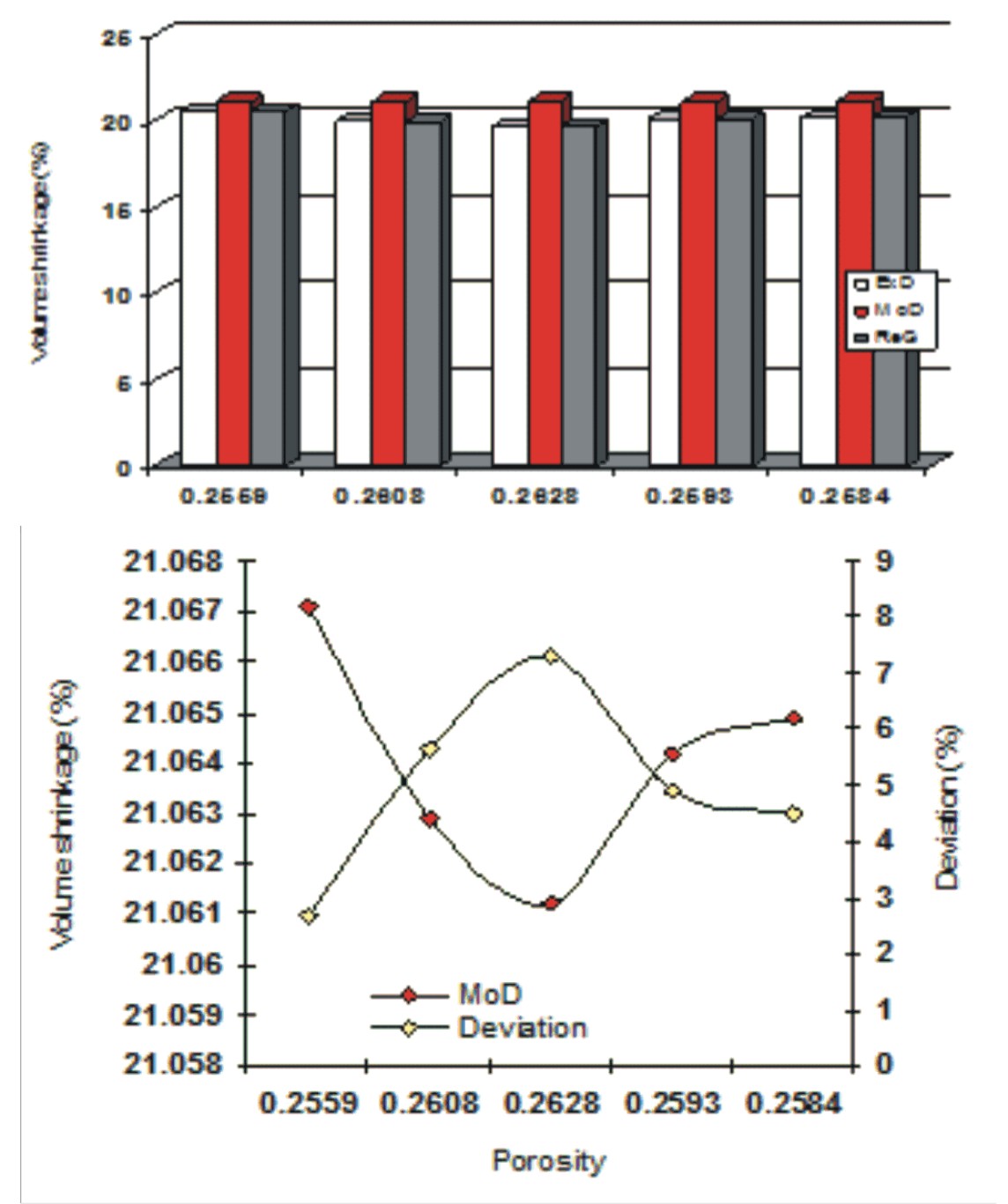
The empirical analysis of ceramics ware shrinkage was carried out, based on the operational influence of firing temperature and sustained porosity. This followed derivation of a model expression relating the post-fired volume shrinkage and firing temperature, and sustained porosity. A clay sample was processed following a well detailed step-wise route. The validity of the derived model expressed as; was rooted in the core expression where both sides of the expression correspondingly approximately equal. Results generated from both experiment and model prediction indicated that post-fired volume shrinkage increases with decrease in the sustained porosity even when the firing temperature is constant. Evaluated results indicated that the correlations between post-fired volume shrinkage and sustained porosity and the standard error incurred in predicting post-fired volume shrinkage for each value of the sustained porosity considered, as obtained from experiment, derived model and regression model were all > 0.9 as well as 0.0307, 3.21 x 10-5 and 2.24 x 10-5 % respectively. The maximum deviation of the model-predicted post-fired volume shrinkage (from experimental results) was less than 8%.