Comparative study on the mechanical properties of fillers-recycled low-density polyethylene for printers and car parts production
Keywords:
Ground shell flour, date palm wood flour, fillers-recycled low density polyethylene; comparative study; mechanical propertiesAbstract
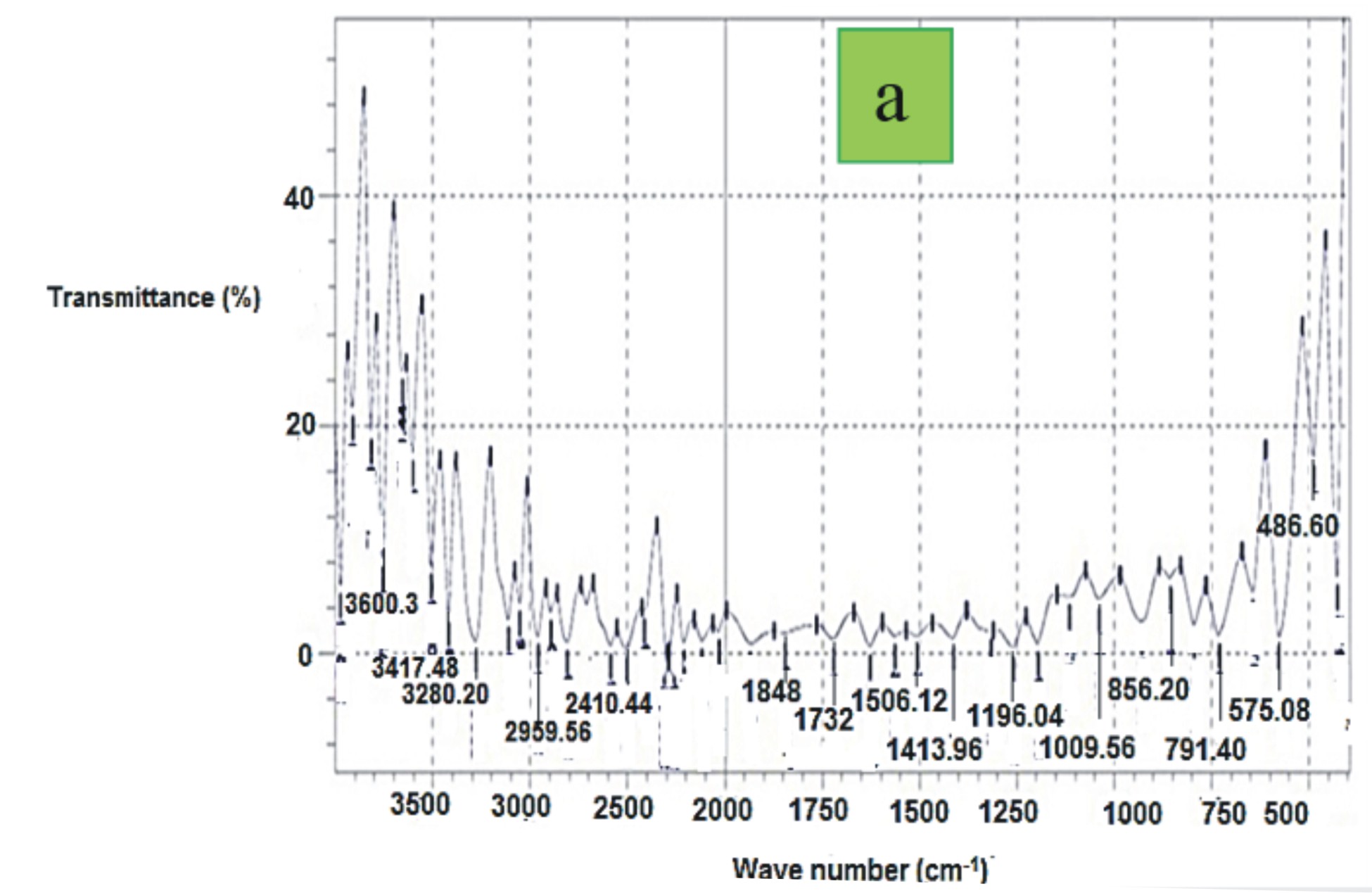
Deposition of biomass and waste plastics into the environment generates adverse consequences to humans. This research was investigated to compare the mechanical properties of groundnut shell flour (GSF) and date palm wood flour (DPWF) on recycled low-density polyethylene (RLDP) composite. The DPWF and GSF at 2-30 wt% were injected in RLDP by injection molding method, respectively. The two fibers were analyzed at four mesh sizes from 150-300 µm. The mechanical characteristics of the DPWF and GSF-RLDP composites analyzed were tensile strength (TST), tensile modulus (TMO), elongation (ELO), flexural strength (FST), flexural modulus (FMO) and Izod impact energy (IIME), respectively. Tensile and flexural properties of the composites were determined using tensometer of TUC-100 model and impact strength was studied by impact tester of LS102 DE model. At ultimate mechanical properties of the composites, FTIR and SEM analysis were conducted to reveal composites structural and morphological behaviours. The TST, TMO, FST, FMO, IIME of DPWF-RLDPE and GSF-RLDPE composites improved with addition of DPWF and GSF in RLDPE matrix with the exception of ELO for both properties, respectively. The results indicated that at 250 µm and 30 wt% of fibers in RLDPE matrix, DPWF-RLDPE composite yielded enhanced micro-mechanical characteristics than GSF-RLDPE composite. At this optimum size of the mixture, the TST, TMO, ELO, FST, FMO and IIMO were 9.56 MPa,, 7.55 %, 1.36 GPa, 46.66 MPa, 1.818 GPa, 1.819 GPa and 2 KJ/m for DPWF-LDPE composite, respectively. Furthermore, the GSF-RLDPE composite corresponded to 8, 50 MPa, 12.50 %, 0.94 GPa, 44.45 MPa, 0.84 GPa and 1.21 KJ/m for TST, TMO, ELO, FST, FMO and IIME, respectively. DPWF exhibited explicit mechanical properties than GSF in RLDP matrix for this study as was justified in the result at optimum size of the filler. DPWF exhibits high mechanical properties of composites compared with GSF in RLDP matrix. The mechanical properties of the composites increase with increased filler content. High tensile and flexural properties were obtained at 250 µm and the impact strength was obtained at 300µm. The result of FTIR and SEM for this study justified the results of mechanical properties at optimum size and content of the filler. DPWF possesses good performance when compared with GSF in the production of composites of RLDP for structural and domestic uses. Hence reduces the environmental danger to human through waste disposal. The DPWF-RLDP composite is recommended to be applied in car parts than GSF-RLDP composite at optimum.