Experimental Design, Characterization, coupling and calibration of type k thermocouple
Keywords:
characterization, coupling, calibration, type-k thermocouple, low voltage applicationAbstract
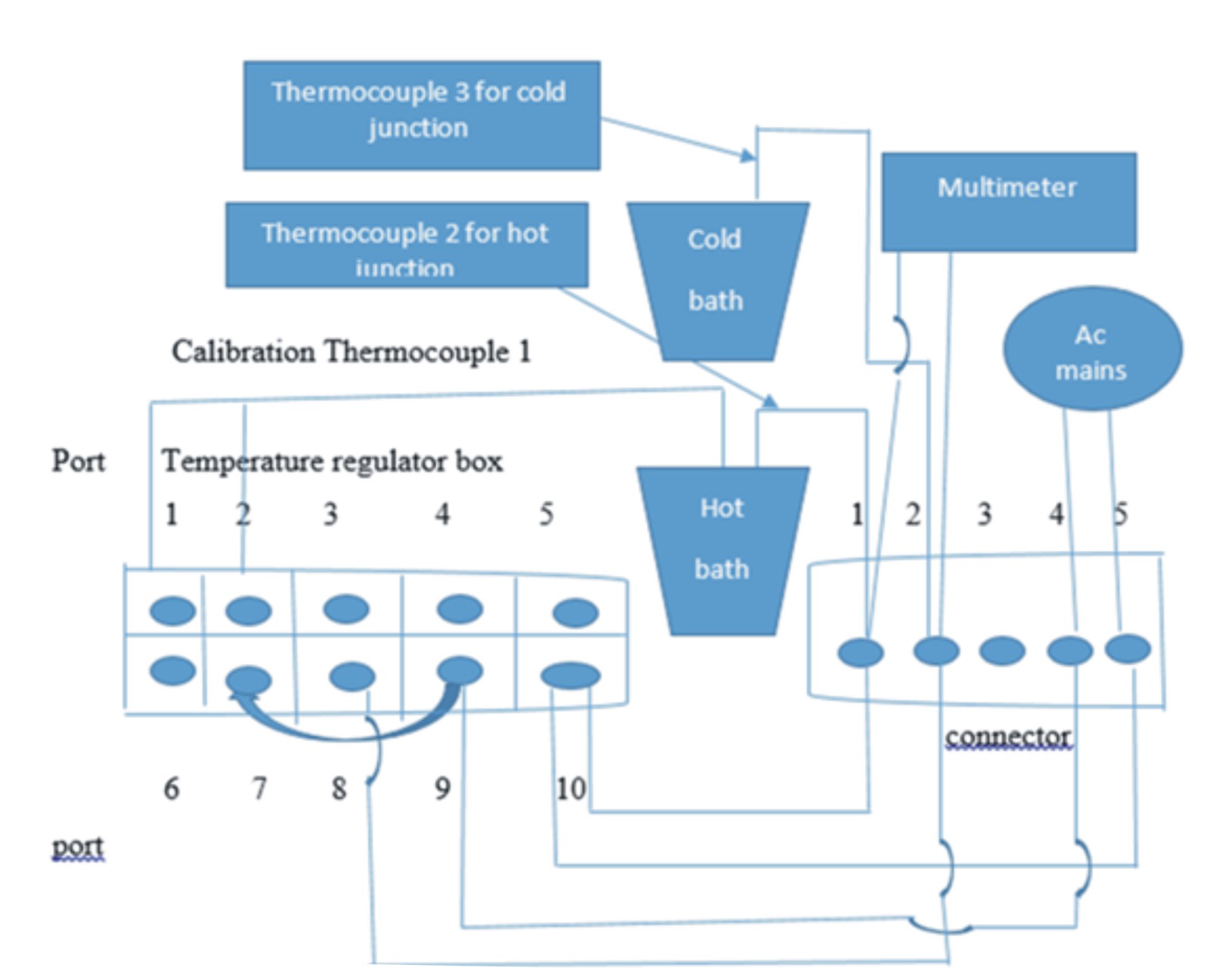
There has been a gap in using type-k thermocouple to produce a low, but still significant voltage, to be utilized in low voltage applications that deal with temperature control. Therefore, there is need to understand the inner workings of thermocouples to ascertain its incorporation into various system applications. This work focused on the characterization, coupling and calibration of the thermocouple in this context, the type-k thermocouple, to see how it will perform under certain temperature conditions in terms of its voltage output. This work designed an experimental method for the characterization, coupling and calibration of type-k thermocouple using Thermal Bath and temperature regulator method as control circuit. Three type-k units were deployed to exploit the hot and cold junction of the device in order to produce a low but significant voltage. A second heat source, the soldering iron, was utilized using 4 type-k thermocouples. For the Thermal Bath, a range of designated variables were considered for a temperature value between 65ºC and 100 ºC. The optimal power peak temperature was pegged at 76 ºC for the Thermal Bath and temperature regulator method. A maximum voltage of 3700 µWatts was produced with a power output of 0.00925 µWatts. The result of using soldering iron as heat source method produced a voltage output of 57900 µV and a power output of 0.06 watts. This concluded the premise that type-k thermocouple could be utilized for low voltage applications such as systems that deploy operational amplifier, digital multimeter and fire alarm sensors for buildings without needing the grid to power the sensor. It also could be observed that the higher the temperature of the heat source, the higher the power output making the type-k thermocouple favorable for nuclear plant application. The minor setback was obtaining the right multimeter to get a voltage reading.