An enhanced fuzzy based Mobile Number Portability (MNP) migration platform in Nigeria
Keywords:
Tariff plan, Call quality factor, Customer care services, Network coverage, Fuzzy, MNPAbstract
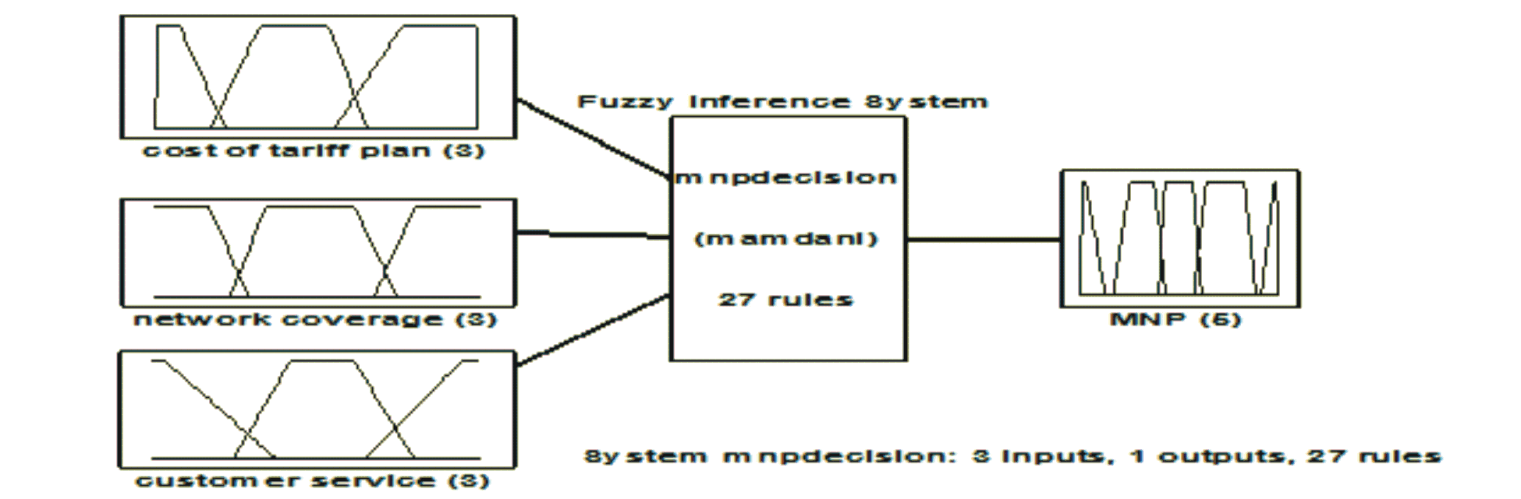
The paper presents an enhanced fuzzy based MNP migration platform in Nigeria. The parameters that could determine why customers would switch their operators are practically tariff plans, call quality factor, customer care services and network coverage parameters. In this research, these four parameters were used for MNP decision using fuzzy logic. On the basis of these four parameters, the decision whether MNP is to be done or not is considered. The tariff plan, call quality factor, customer care services and network coverage are input parameter and MNP is output parameter. Input parameter tariff plan gives the information of call rate per naira. Tariff plan was taking from minimum of 5 available tariff plans to a maximum of 15 available tariff plans. The whole range were distributed in three levels: small, medium and large. Based on the rule base decision rules, a fuzzy logic 3D surface diagrams were used for the result analysis. The results showed that a cheap tariff plan indicates a high MNP decision allowing the user to port to the test network. When the tariff plan is expensive and the MNP decision is low, the user decides not to port to the test network. When a user considers network coverage and cost of tariff plan, MNP decisions are usually difficult to make. This is because strength of network coverage does not determine the cost of the tariff plan to be used, that is in the case of WLAN networks in Nigeria. Therefore, from the research concludes that a cheap Tariff leads to a high MNP value, while an expensive tariff makes a low MNP decision. This approach demonstrates the replaceability of the existing GSM architecture with an adequate trusted computing model for all mobile network operators in the mobile communication value chain.