Fault Diagnosis on a 330kV Power System Transmission Line Using Integrated S-Transform, Artificial Neural Network and Travelling Wave Techniques
Keywords:
S-Transform, Pattern Recognition, Travelling Wave, Waveform and SignalAbstract
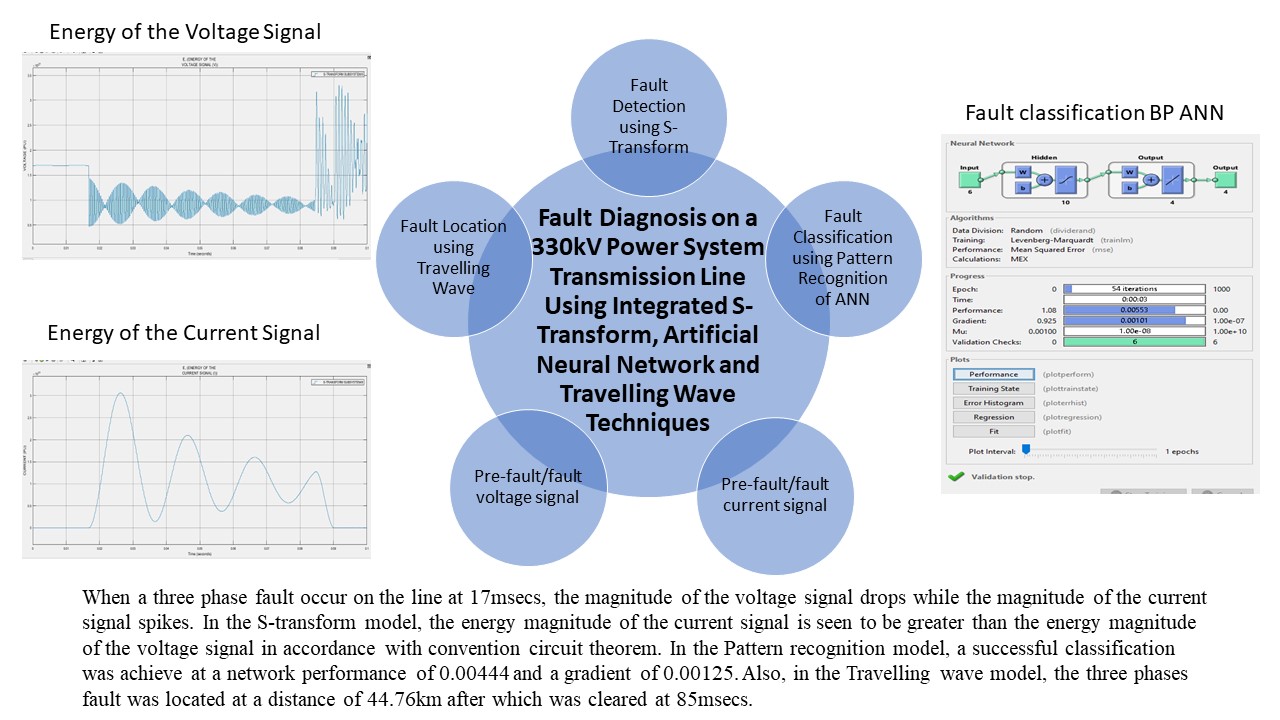
Due to the frequent and unpredictable occurrence of fault in our power transmission system, a need for the method intelligent enough to identify, categorize, and locate faults becomes imminent so as to ensure and guarantee an optimal reliability of the protection system of the transmission system/network. This paper presents an integral approach for fault diagnosis using a time-frequency (S-Transform) technique for fault detection, an Artificial Neural Network (ANN) called Pattern Recognition Algorithm for fault classification and a Travelling Wave technique for fault location on 47.39km Ajaokuta to Lokoja 330kV transmission line based on MATLAB/SIMULINK simulation and analysis. The S-Transform method employs a scalable and moving localizing Gaussian window to identify fault using the energy of the voltage and current signals, the chosen ANN classification network makes use of the pre-fault and fault voltages and current data to train the neural network to be able to classify fault and the Traveling wave approach uses the line voltage, current, propagation velocity, inductance, capacitance and length of line to find the fault distance. Various fault types were simulated on MATLAB/SIMULINK software and for each, the value of current magnitude of the energy signal were greater than the value of the voltage magnitude of the energy signal in accordance to conventional circuit theorem, a successful fault classification with a good performance and gradient value and the fault distance located along the transmission line.