Assessment of Flooding Impact of River Ngadda in Borno State
Abstract
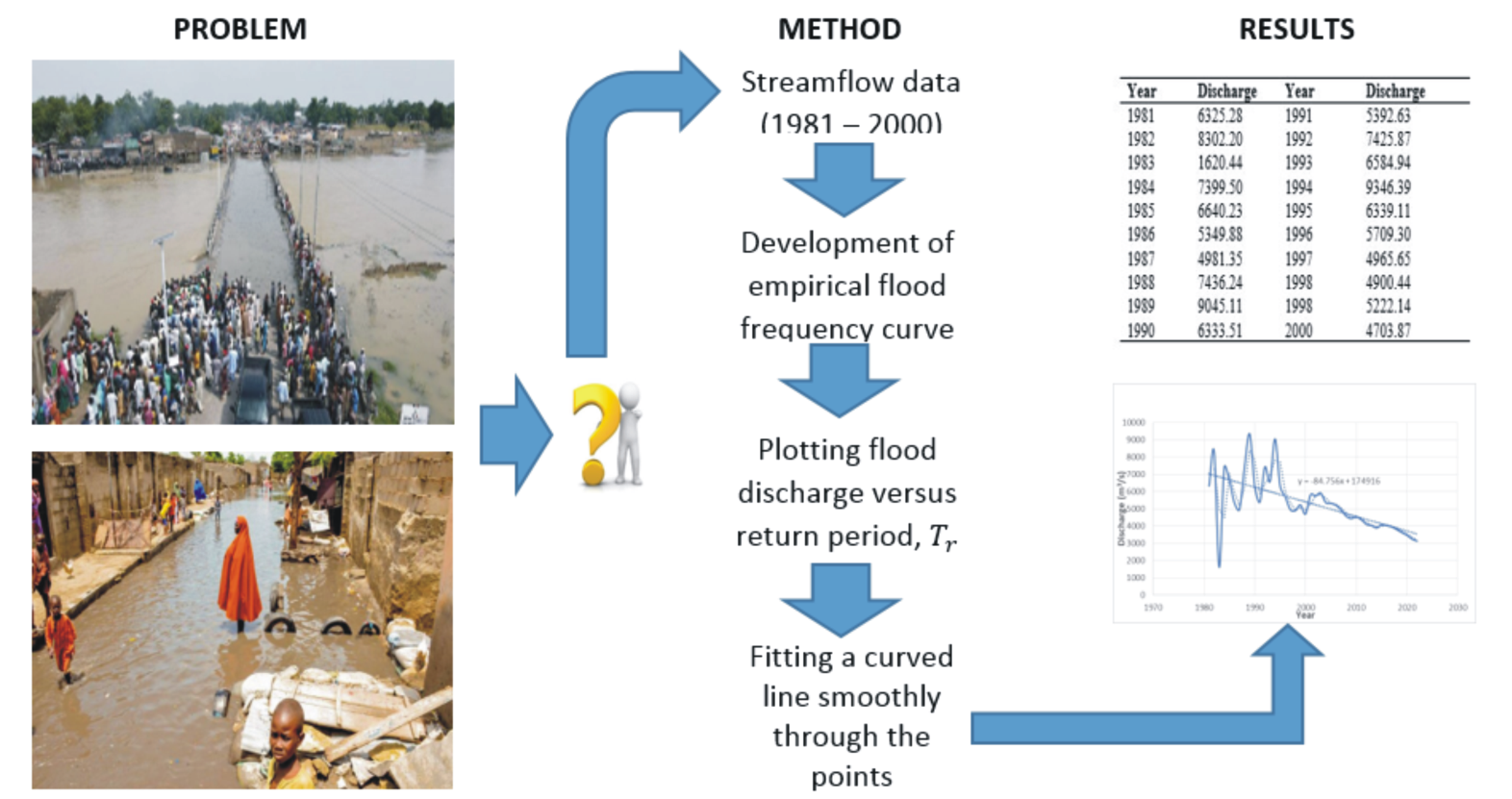
Flooding is a threat to the environment that requires appropriate measures to be taken to mitigate it effects. Flood frequency analysis of River Ngadda was carried out using available historical streamflow data (1981 – 2000). Preventive measures to mitigate the impact of flooding were also proposed. Statistical analysis revealed that River Ngadda experienced flood in 7 years from the period of 1981 to 2000 with an annual mean flow discharge of 7728.7m3/s and skewness of 0.86. Furthermore, results showed that River Ngadda experienced another 7 years of flood from the period of 2001 to 2022 with annual average streamflow and skewness of 4241.44m3/s and 1.04 respectively. To this end, the present study suggested that government should ensure compliance to the environmental management policies that are properly enforced in the country. Equally, development control activities should be taken seriously to avoid erecting on flood plains and flood-prone areas. Finally, regular environmental education should be given priority in society as it is always ascribed that knowledge is power, and with power, there is no limit to achievement.