Biochemical oxygen demand prediction model from chemical oxygen demand cum-extra principle parameters values in selected fish ponds wastewater around Nekede
Keywords:
BOD, COD, Model, fish, pond, wastewater, physicochemicalAbstract
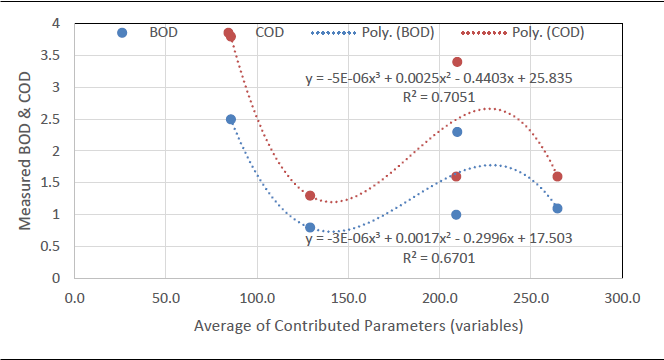
Water is the most fundamental substance for the life and sustainability of terrestrial and aquatic organisms. Few issues have a greater impact on human lives in the life of the planet than on the management of the most important natural resources. The study was carried out using fish farming ponds selected around Nekede. Wastewater samples were harvested from five different artificial pond sources. The collected wastewater sample was tested for the following physicochemical parameters. PH. Temperature, BOD, and COD at the water laboratory. The two models one BOD with the expression and COD with the expression were successfully obtained through least regression process. For correlation analysis, the predictions were plotted against measured values and the r2 values obtained are 0.9 and 0.8 which shows a strong relationship. Based on the model fitting comparison analysis using the Student-t test, the null hypothesis Ho was accepted, indicating no significant difference between the measured and predicted BOD and COD values, thus confirming the model's accuracy. Other parameters of the fishpond which include the volume of the pond, quantity of fish, density, feeding quantity per day, duration of the wastewater, and the GPIS data of those ponds were all measured. The COD parameter value was transformed into a model to predict the BOD parameter of pond wastewater. Two models were developed to accurately predict BOD or COD separately, using the measured values of other parameters, for fishpond wastewater.