Hysteresis of polyamide 12/ethylene propylene diene monomer polymeric blends filled with nano-clay under cyclic loading: Experimental approach
Keywords:
hysteresis, blends, nano-clay, cyclic loading, stress relaxation, Mullin's effectAbstract
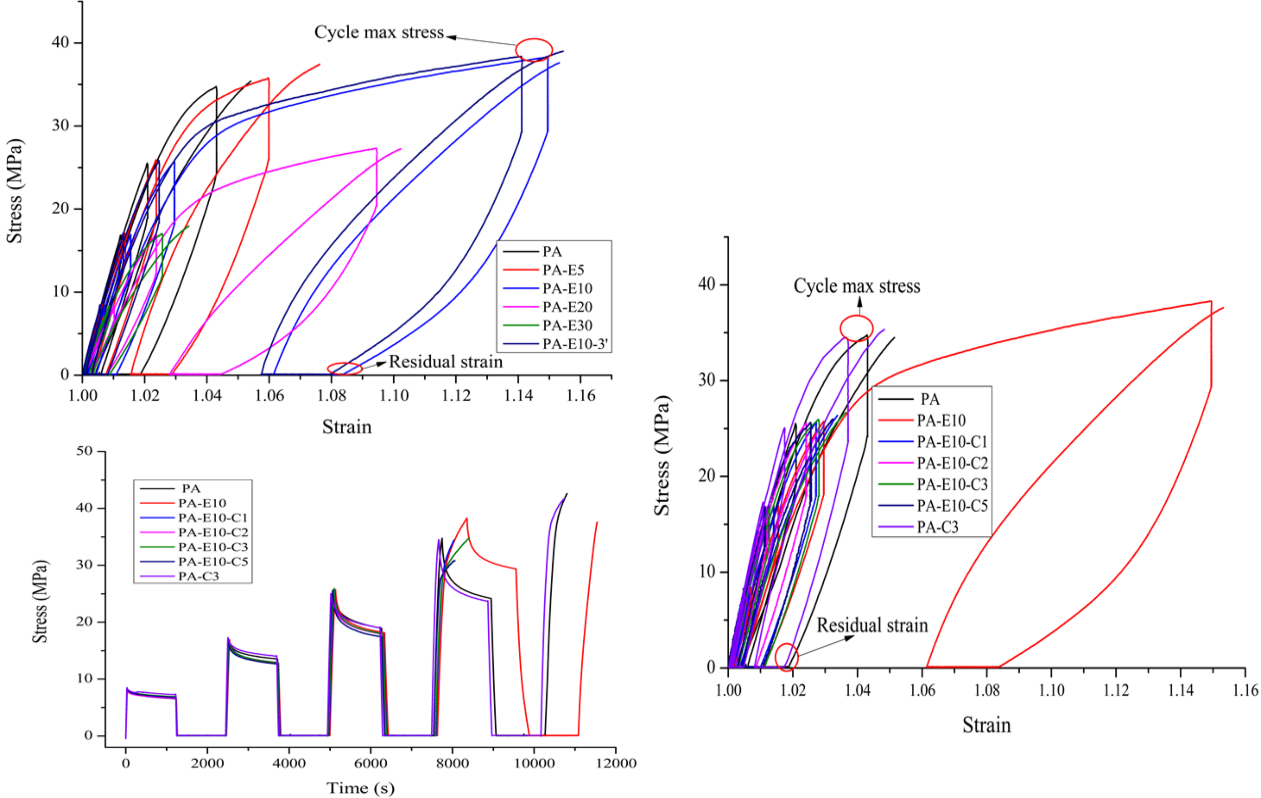
Polyamide 12 (PA12) is a type of polymer extensively used in many applications due to its strength, low water absorption and density. Blending PA12 with elastomers and other consumer polymers expand its applications. Pure ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) is soft and elastic, which limits it load bearing applications. To overcome such limitation, PA12 and EPDM can be greatly improved by reinforcing the matrix with Cloisite 30B (C30B). The only objective is to determine the Mullins effect of EPDM and C30B when blended with PA12. The three constituents were simultaneously mixed by using an internal mixer (Haake Rheomix 600) at a blade rotational speed of 100 rpm, during 6 or 3 mins, at 200 ºC. To minimize the degradation of the composite components during mixing, especially the alkyl ammonium ions, the processing temperature was fixed at 200 ºC, which corresponds to less 20 0C above the melting point of PA12. All samples were pelletized by compression moulding at 200 ºC between 2 mm thick plates, at several C30B mass fractions ranging from 0 to 5 w.t%. Cyclic tension tests are conducted to probe the hysteretic action of the C30B composites. The results show that the stress increased in a separate manner from 10 MPa to 40 MPa. This clearly implies that an increase in the stress response can be realized by increasing the w.t % of either EPDM in the binary composites or C30B in the ternary nanocomposites, meaning that EPDM or C30B can potentially affect the mechanical response. In all the composites, a clear Mullins effect can be noticed as the stress in the reloading operation is lesser than the response of the virgin specimens until striking the beginning of maximum applied strain. Also, a smaller hysteresis loop can be noticed with increase in the amount of C30B into the pure PA12 blend. This work can likely add to understanding the properties of PA12 filled with EPDM and C30B particles and dignify the applications.