Assessment of constraints to mushroom production and scientific training needs of mushroom farmers in Oyo state Nigeria
Keywords:
Science, Mushroom, Cultivation, Credit and ConstraintsAbstract
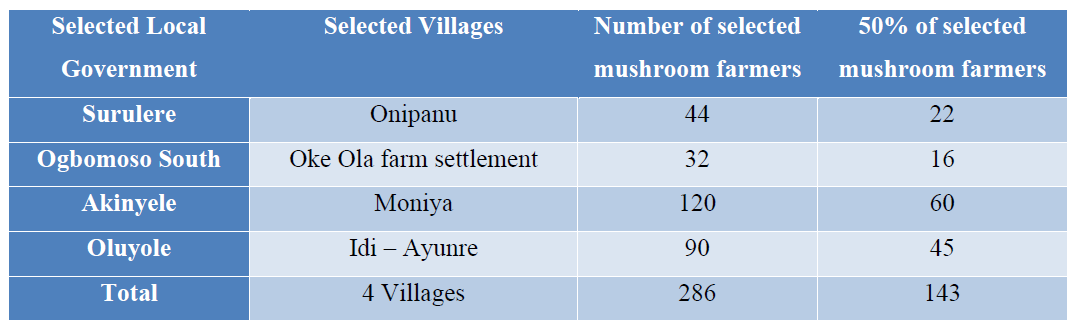
In many parts of the world, edible mushrooms are utilized for medicinal purposes and they also served as food and vegetable. Mushroom cultivation is an efficient method of disposing agricultural waste and means of producing nutritious food in most part of Nigeria, Mushroom production is another easiest ways of earning a stable income during adverse condition caused by climate change, Involving science in mushroom training enhances understanding and optimization of mushroom cultivation. Therefore, the study assess the constraints to mushroom production and scientific training needs of mushroom farmers in some selected villages in Oyo State, Nigeria, with the following objectives; examine the socioeconomic characteristics of mushroom farmers, examine the enterprise characteristics of mushroom farmers, examine their levels of scientific skill in mushroom production, identify constraints to mushroom production in the study area. Four (4) Local Governments Areas were selected randomly for this study and mushroom farmers were selected purposeful in each village. (50%) of the farming households were randomly selected to give a total sample size of 143 respondents. Data was obtained with the aid of well-structured questionnaire, complemented with schedule interviewed. Descriptive and inferential statistical tools were used to analyze collected data. The results shown that; most of the respondents were young (38.5%), male (63.00%) mushroom farmers between the age of 35 and 44 years, most of the respondents were married (81.80%), with source of credit from personal savings (49,00%), cooperative society (23.80%) and family and friends (17.50%). The respondents are skillful in substrate technology (93.00%), production (86.00%), packaging (79.00%), marketing (72.00%) and storage (64.30%) skills. Main constraints faced by the mushroom farmers were poor marketing channel (72.70%), lack of access to credit facilities (71.30%) and inadequate information (68.50%) on mushroom cultivation. The Pearson Product Moment Correlation (PPMC) analysis shown that, there is significant relationship between the scientific training needs and constraints faced by farmers, From the results so far, it is recommended that Research Institute and Extension agents, should disseminate timely and up–to–date information to farmers on mushroom cultivation. Establishment of farmers’ co-operative society among farmers will go a long way in having access to soft loan.