Prediction of Heart Disease using Autoencoder with LightGMB and Gradient Boosting
Keywords:
Cardiovascular Disease, Autoencoder, LightGBM, Gradient BoostingAbstract
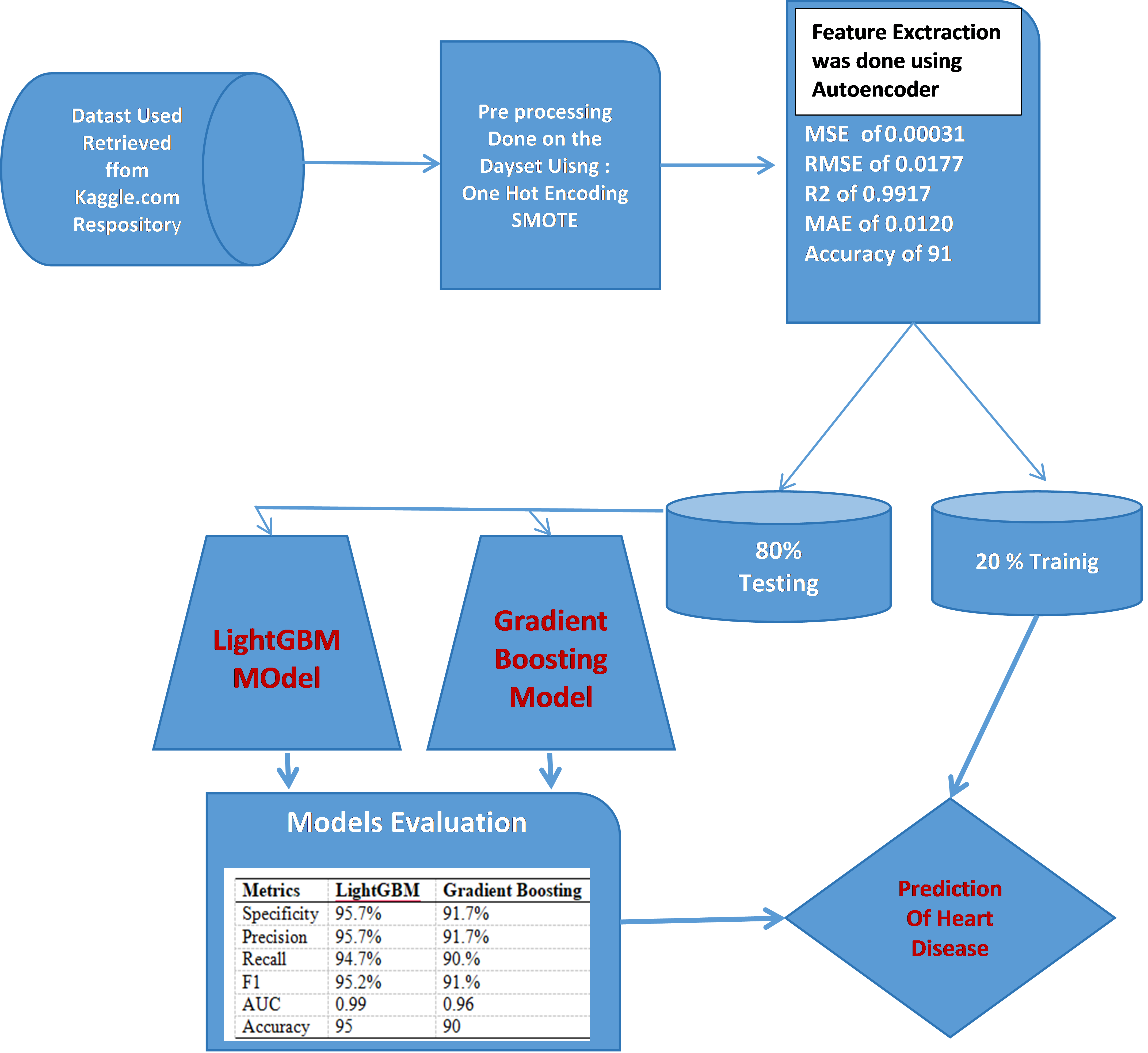
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) refers to heart disease. CVD is seen to cause majority of death in world. Because of this problem many researchers have been drawn to this area to develop models and systems to predict occurrence of heart disease for early treatment. This study developed a Heart disease predicative model using Autoencoder with LightGBM and Gradient Boosting. The Dataset used was gotten from kaggle.com. One Hot Encoding, SMOTE were used to pre-processed the dataset. Feature extraction was done using Autoencoder. Two classification methods: LightGBM and Gradient Boosting were employed to build the predictive model. The result shows that Autoencoder perform very well with low values of MSE, RMSE, MAE and High Value of F2 score. The result of LightGBM shows a specificity of 95.7%, precision value of 95.7%, recall value of 94.7% ,F1 value of 95.2% , AUC value of 0.99 and Accuracy value of 95 While the results of Gradient Boosting shows Specificity of 91.7%, Precision value of 91.5%, Recall value of 90.0% ,F1 value of 91.0% , AUC value of 0.96 and Accuracy value of 90. The study concluded that LightGBM perform better that Gradient Boosting. The Model is recommended to the health sector management to guide their decision making. Its potential integration with predictive model and clinical validation will assist greatly in improving the heart disease diagnosis and prevention. Further research could be done with more validating metrics, more deep learning techniques.