Adsorptive Removal of Azo Dye from Aqueous Solution Using Sustainable Material: Equilibrium, Kinetic, and Optimization Analysis
Keywords:
adsorption, dye, equilibrium, kinetic, modeling, thermodynamicsAbstract
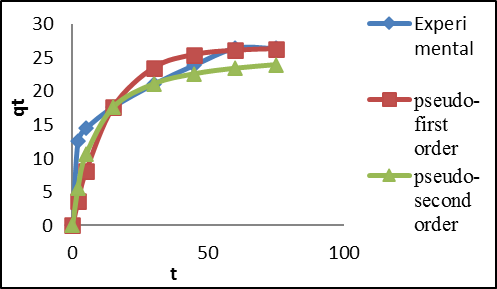
Dyes are colored substance of environmental concern due to their negative impacts on the water quality of both surface and ground water. This research focused on removal of Congo-red dye (CR) from effluent using the adsorptive qualities of Awka raw clay (ARC). The batch system was applied to evaluate the effect of process-independent variables. The thermodynamic properties ΔS, ΔH, ΔG, and Ea were determined. The optimum CR removal was predicted using the RSM model. Maximum percentage dye removal and adsorption capacity of 66% and 26.41 mg/g respectively were obtained via batch adsorption system. Thermodynamic results confirm the CR adsorption as endothermic, spontaneous, and physical process. The RSM model, with R2 of 0.9982 confirmed the model prediction statistically accurate. These obtained results confirm ARC cost-effective adsorbent for CR removal from effluents.