Interfacial Adhesion and Physicomechanical Behaviours of Optimally Acetylated Kapok Fiber–Polymethylmethacrylate Composites for Prosthodontic Applications
Acetylated kapok fiber reinforced polymethylmethacrylate denture base material
Keywords:
Kapok fiber, acetylation, Polymethyl methalcrylate, interfacial adhesion, water absorptionAbstract
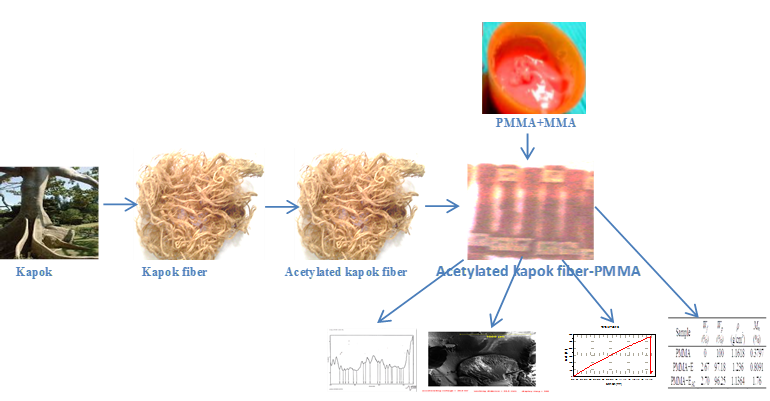
Interfacial adhesion and physicomechanical behaviours of optimally acetylated kapok fiber–polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) composites for prosthodontic applications was investigated. Kapok fiber was extracted using water retting technique and chemically modified using acetic anhydride. The central composite design of response surface methodology (RSM) was employed to optimize the kapok fiber modification using 3-15 % of acetic anhydride and 30-150 minutes. Polymethyl methacrylate denture base material (95.25-99.25%) was modified with optimally acetylated kapok fiber (0.75-3.75%) and optimized based on tensile, flexural, hardness and impact properties. The density, water absorption and water absorption kinetics were determined. At optimum preparation of acetylated kapok fiber-PMMA, the tensile strength, hardness and interfacial adhesion were improved by 13.16, 8.06 and 67.93%, respectively, with reduced flexural strength (49.62%) and modulus (65.18%), and impact strength (22.52%). Acetylation reduced the density and water absorption of kapok fiber-PMMA by 8.6 and 117.53 %, restored the non-fickian water absorption behaviours and reduced coefficient. Hence optimized acetylated kapok fiber-PMMA denture base material enhanced the quality and durability with reduced residual monomer that may lead to cytotoxicity of oral cavity.