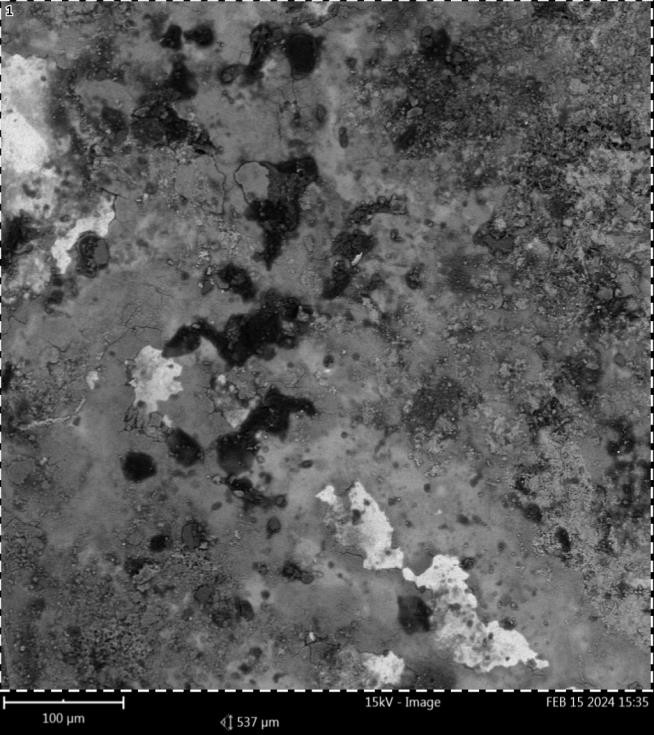
Enhancing the Corrosion Protection of Mild Steel using Nickel-Voltage-Controlled Electrodeposition
Keywords:
Corrosion, electrodeposition, coating voltage, surface morphology, protective filmAbstract
Tailoring the electrodeposition parameters to yield high performance coating for corrosion control in mild steel is important for its sustainability as an effective corrosion mitigation measure. Nickel film was electrodeposited on mild steel for corrosion inhibition at varied coating voltages. The influence of the coating voltage on the surface morphology with elemental percentage composition and the corrosion resistance of the coating was examined using scanning electron microscopy/energy dispersive spectroscopy (SEM/EDS) and potentiodynamic polarization method respectively. Results obtained showed that the electrodeposited nickel film impacted an impressive corrosion inhibitory property on mild steel when compared to the uncoated samples. The study also indicated that corrosion rate of 0.0074996 mm/yr, 0.0005916mm/yr, and 0.00440 mm/yr where obtained with coating voltage values of 2, 4 and 7Volts respectively. This indicates that the coating voltage has significant effect on the corrosion resistance potential of nickel film. The optimal corrosion resistance performance of the coating material was achieved using coating voltage of 4Volts which yielded corrosion inhibition efficiency of 97.7%. The morphology of the samples deposited using the optimal setting indicated smoother surfaces with minimum corrosion affected areas in contrast to the one coated using extremely low and high voltage values. Thus, an optimal electrodeposition voltage at which nickel-coated mild steel exhibits significantly enhanced corrosion resistance has been identified. More also the correlation between the electrodeposition voltage, microstructural characteristics and the corrosion protective film integrity has been established. Hence, optimizing a single electrochemical parameter-coating voltage, is a cost- effective approach for enhancing the durability and sustainability of mild steel in corrosive environments for industrial applications