Influence of Fuel Types and Additives on the Efficiency of Catalytic Converter Materials in Automotive Applications
Keywords:
Fuel type additives, catalytic converter, materials efficiency, and automobiles applicationsAbstract
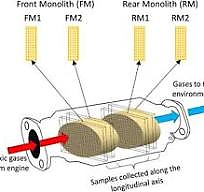
The increasing demand for sustainable and low-emission transportation has intensified research into improving the efficiency of catalytic converters (CCs) in automotive applications. One critical challenge lies in understanding how different fuel types and the incorporation of various additives influence the performance and longevity of CC materials. This study aims to investigate the impact of conventional and alternative fuels, along with specific fuel additives, on the thermal stability, conversion efficiency, and degradation behavior of CCs. A combination of thermo gravimetric analysis (TGA), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) was employed to examine the structural and compositional changes in the catalyst materials. Engine bench testing and exhaust emission analyses were also conducted to evaluate real-time performance. The results revealed that fuel composition significantly affects the catalytic activity, with certain additives enhancing oxidation reactions while others accelerate material degradation. Converters exposed to biofuel blends exhibited improved NOx and CO conversion efficiencies, while metal-based additives led to notable sintering and poisoning effects. It is recommended that future automotive fuel formulations be optimized not only for combustion efficiency but also for compatibility with advanced catalytic materials to ensure prolonged converter life and reduced environmental impact.